In my role as a curriculum coordinator, teachers frequently ask me what digital literacy is and how to integrate it. Of course, being both an umbrella term for multiple literacies and an emerging fad term in education, digital literacy is being interpreted in a variety of ways. Consequently, I find teachers usually need resources that:
In my role as a curriculum coordinator, teachers frequently ask me what digital literacy is and how to integrate it. Of course, being both an umbrella term for multiple literacies and an emerging fad term in education, digital literacy is being interpreted in a variety of ways. Consequently, I find teachers usually need resources that:
- Clarify what digital literacy is in both a British Columbiana and Canadian context;
- Connect digital literacy to the broader international context;
- Offer practical information around the BC Privacy Laws;
- Offer relevant virtual tools and resources for students that cover the three digital literacy principals: use, comprehend, create.
I have put together a Symbaloo pathway with a sampling of these resources. I have chosen the collected sites based on quality, context and BC teacher need. In terms of quality, where possible, I have vetted resources that are based on research and a clear understanding of what digital literacy is, I have included critical resources for BC teachers such as the BC Digital Literacy Standards and the BC Privacy Laws (Cloud Computing for Public Bodies). Also, as many teachers request virtual tools to explore the different aspects of digital literacy, I have included sites with tools and lesson ideas as well as some BC educational blogs to provide pedagogical context for those tools. Hopefully there is something for everyone! By no means is this collection exhaustive and I would be grateful if anyone could suggest more relevant sites. Click on the picture below to explore the collection.
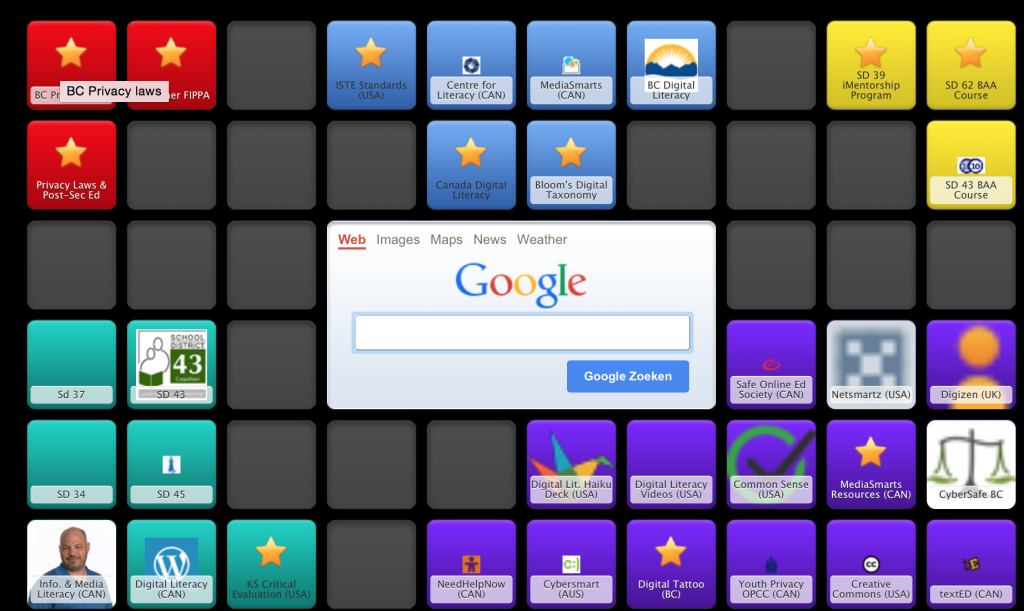
Highlighted Sites
Media Awareness Network. (2010). Digital Literacy in Canada: From Inclusion to Transformation
If you read only one resource on digital literacy, make this it. It gives a concise and accurate summary of what digital literacy is based on research and outlines how and why it is necessary within a Canadian context.
Ministry of Education. (2014). BC’s Digital Literacy Framework
Did you know that we have a digital literacy framework complete with an official definition, characteristics (aka. competencies) and student profiles? Although potentially useful, the characteristics and profiles are derived from the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE) Standards. In many cases the language is verbatim. Although a start, in my opinion, the framework is a discordant mix of different ideas pulled from diverse places rather than a comprehensive work guided by a clear and contextualized vision. I’m excited to see what this beginning might evolve into.
Hengstler, Julia. (2013). A K-12 Primer for British Columbia Teachers: Posting Students’’ work Online.
A practical guide for teachers on how to navigate the BC privacy laws for public bodies (i.e. public schools).
MediaSmarts: Canada’s Center for Digital and Media Literacy.
If you are looking for resources and lesson ideas and only have time for a one-stop shop, this is it. Quality and Canadian.
Abbotsford School District. Digital Literacy and Citizenship Curriculum K-12
Looking for BC grade specific virtual tools/websites for digital literacy? Curated with an eye to BC’s Digital Literacy Framework, there is something for everyone here.
Board/Authority Authorized (BAA) Courses
BAA courses are courses that have been developed within a district to meet local needs. These courses can be used for the 28 credits of electives required for graduation (grades 10-12). Any district can submit a BAA course for approval in their own district. If you are interested in offering a digital literacy course in your district, you could use a BAA course already developed or develop your own. Two digital literacy BAA courses developed are available here. If you know of more, please comment below!
 n light of the possible consequences of ignorance . . .
n light of the possible consequences of ignorance . . .